AC会议论文平台致力于为国际学术会议组织者及参与者提供高效、稳定的全流程论文管理服务。我们支持论文提交、评审、收录和出版等环节,保障学术交流的严谨与顺畅。
学术会议












近期截稿会议












CCF推荐
| 名称 | 类别 | 年份 | 开会日期 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ASPLOS: Architectural Support for Programming Languages and Operating Systems | A类 | 2026 | 2026-03-22 |
| EuroSys: European Conference on Computer Systems | A类 | 2026 | 2026-04-13 |
| DATE: Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference | B类 | 2026 | 2026-04-20 |
| RTAS: Real-Time and Embedded Technology and Applications Symposium | B类 | 2026 | 2026-05-12 |
| IPDPS: International Parallel & Distributed Processing Symposium | B类 | 2026 | 2026-05-25 |
| HPDC: ACM Symposium on High-Performance Parallel and Distributed Computing | B类 | 2026 | 2026-07-13 |
| SPAA: ACM Symposium on Parallelism in Algorithms and Architectures | B类 | 2025 | 2026-07-28 |
| ISPD: International Symposium on Physical Design | C类 | 2026 | 2026-03-15 |
| 名称 | 类别 | 年份 | 开会日期 |
|---|---|---|---|
| NSDI: Symposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation | A类 | 2026 | 2026-05-04 |
| INFOCOM: IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications | A类 | 2026 | 2026-05-18 |
| MobiCom: ACM International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking | A类 | 2026 | 2026-11-25 |
| SenSys: ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems | B类 | 2026 | 2026-05-11 |
| MobiSys: International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services | B类 | 2026 | 2026-06-21 |
| WCNC: IEEE Wireless Communications & Networking Conference | C类 | 2026 | 2026-04-13 |
| ICC: IEEE International Conference on Communications | C类 | 2026 | 2026-05-24 |
| MSN: International Conference on Mobility, Sensing and Networking | C类 | 2026 | 2026-12-03 |
| 名称 | 类别 | 年份 | 开会日期 |
|---|---|---|---|
| EUROCRYPT: European Cryptology Conference | A类 | 2026 | 2026-05-10 |
| S&P: IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy | A类 | 2026 | 2026-05-18 |
| FSE: Fast Software Encryption | B类 | 2026 | 2026-03-23 |
| PKC: International Workshop on Practice and Theory in Public Key Cryptography | B类 | 2026 | 2026-05-25 |
| FC: Financial Cryptography and Data Security | C类 | 2026 | 2026-03-02 |
| DFRWS-EU: Digital Forensic Research Workshop | C类 | 2026 | 2026-03-23 |
| DFRWS EU: Digital Forensics Research Workshop EU | C类 | 2026 | 2026-03-24 |
| EuroS&P: IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy | C类 | 2026 | 2026-07-06 |
| 名称 | 类别 | 年份 | 开会日期 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ICSE: International Conference on Software Engineering | A类 | 2026 | 2026-04-12 |
| ESEC/FSE: ACM Joint European Software Engineering Conference and Symposium on the Foundations of Software Engineering | A类 | 2026 | 2026-07-05 |
| OOPSLA: Conference on Object-Oriented Programming Systems, Languages, and Applications | A类 | 2026 | 2026-07-17 |
| ISSTA: The International Symposium on Software Testing and Analysis | A类 | 2026 | 2026-10-03 |
| SANER: IEEE International Conference on Software Analysis, Evolution and Reengineering | B类 | 2026 | 2026-03-17 |
| ICPC: International Conference on Program Comprehension | B类 | 2026 | 2026-04-12 |
| REFSQ: Requirements Engineering: Foundations of Software Quality | C类 | 2026 | 2026-03-23 |
| WICSA: IEEE International Conference on Software Architecture | C类 | 2026 | 2026-06-22 |
| 名称 | 类别 | 年份 | 开会日期 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ICDE: International Conference on Data Engineering | A类 | 2026 | 2026-05-04 |
| SIGMOD: ACM Conference on Management of Data | A类 | 2026 | 2026-05-31 |
| EDBT: International Conference on Extending DB Technology | B类 | 2026 | 2026-03-24 |
| ICDT: International Conference on Database Theory | B类 | 2026 | 2026-03-24 |
| PODS: ACM SIGMOD Conference on Principles of DB Systems | B类 | 2026 | 2026-05-31 |
| ECIR: European Conference on Information Retrieval | C类 | 2026 | 2026-03-30 |
| ESWC: Extended Semantic Web Conference | C类 | 2026 | 2026-05-10 |
| PAKDD: Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining | C类 | 2026 | 2026-06-09 |
| 名称 | 类别 | 年份 | 开会日期 |
|---|---|---|---|
| STOC: ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing | A类 | 2026 | 2026-06-22 |
| LICS: Annual ACM/IEEE Symposium on Logic in Computer Science | A类 | 2026 | 2026-07-20 |
| SAT: International Conference on Theory and Applications of Satisfiability Testing | B类 | 2026 | 2026-07-20 |
| CCC: IEEE Conference on Computational Complexity | B类 | 2026 | 2026-08-03 |
| STACS: International Symposium on Theoretical Aspects of Computer Science | C类 | 2026 | 2026-03-10 |
| RTA/FSCD: International Conference on Formal Structures for Computation and Deduction | C类 | 2026 | 2026-07-20 |
| FMCAD: Formal Methods in Computer-Aided Design | C类 | 2026 | 2026-09-14 |
| 名称 | 类别 | 年份 | 开会日期 |
|---|---|---|---|
| IEEE VR: IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces | A类 | 2026 | 2026-03-21 |
| DCC: Data Compression Conference | B类 | 2026 | 2026-03-24 |
| ICASSP: International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing | B类 | 2026 | 2026-05-06 |
| i3D: ACM Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics | B类 | 2026 | 2026-05-15 |
| 3DV: International Conference on 3D Vision | C类 | 2026 | 2026-03-20 |
| CVM: Computational Visual Media Conference | C类 | 2026 | 2026-04-10 |
| PacificVis: IEEE Pacific Visualization Symposium | C类 | 2026 | 2026-04-20 |
| ICIP: International Conference on Image Processing | C类 | 2026 | 2026-09-13 |
| 名称 | 类别 | 年份 | 开会日期 |
|---|---|---|---|
| CVPR: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition | A类 | 2026 | 2026-06-03 |
| ACL: Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics | A类 | 2026 | 2026-07-02 |
| ICML: International Conference on Machine Learning | A类 | 2026 | 2026-07-06 |
| IJCAI: International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence | A类 | 2026 | 2026-08-15 |
| ICRA: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation | B类 | 2026 | 2026-06-01 |
| ICAPS: International Conference on Automated Planning and Scheduling | B类 | 2026 | 2026-06-27 |
| COLT: Annual Conference on Computational Learning Theory | B类 | 2026 | 2026-06-29 |
| AISTATS: International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics | C类 | 2026 | 2026-05-02 |
| 名称 | 类别 | 年份 | 开会日期 |
|---|---|---|---|
| CHI: ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems | A类 | 2026 | 2026-04-16 |
| PerCom: IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications | B类 | 2026 | 2026-03-16 |
| IUI: ACM International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces | B类 | 2026 | 2026-03-23 |
| ICWSM: The International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media | B类 | 2026 | 2026-05-27 |
| ECSCW: European Computer Supported Cooperative Work | B类 | 2026 | 2026-06-29 |
| MobileHCI: International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction with Mobile Devices and Services | B类 | 2026 | 2026-08-31 |
| GI: Graphics Interface Conference | C类 | 2026 | 2026-06-09 |
| DIS: ACM conference on Designing Interactive Systems | C类 | 2026 | 2026-06-13 |
| 名称 | 类别 | 年份 | 开会日期 |
|---|---|---|---|
| WWW: International World Wide Web Conferences | A类 | 2026 | 2026-04-13 |
| RECOMB: International Conference on Research in Computational Molecular Biology | B类 | 2026 | 2026-05-26 |
| ISMB: International Conference on Intelligent Systems for Molecular Biology | B类 | 2026 | 2026-07-12 |
| CogSci: Cognitive Science Society Annual Conference | B类 | 2026 | 2026-07-22 |
| EMSOFT: International Conference on Embedded Software | B类 | 2026 | 2026-10-04 |
| MICCAI: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention | B类 | 2026 | 2026-10-04 |
| ICIC: International Conference on Intelligent Computing | C类 | 2026 | 2026-07-22 |
| AMIA: American Medical Informatics Association Annual Symposium | C类 | 2026 | 2026-11-07 |
学术期刊
学术动态

02-09
绿城春意浓,邕江聚能澜。在这承载着希望与新机的早春时节,第三届智能电网与电力系统国际会议(ICSGPS 2026)于2026年2月1日在中国·南宁隆重开幕。
本次会议由广西大学主办,浙江大学、上海交通大学、武汉大学、武汉理工大学、西南科技大学、东北电力大学、湖南大学、中南大学、西南石油大学、长安大学、爱迩思出版社(ELSP)、ESBK 国际学术交流中心以及AC学术平台联合支持。会议旨在汇聚全球电力能源、智能电网、电力电子及系统集成等领域的顶尖学者、行业专家与青年科研力量,围绕新型电力系统构建、可再生能源并网、电网数字化与智能化等关键议题展开深度交流,共同推动能源电力领域的科技创新与产业协同发展。

会议开幕式
1日上午,会议在南宁永恒朗悦酒店会议厅正式启幕。线上线下来自全球各地的数百位专家学者及青年学子齐聚一堂,共同见证了这一学术盛会的开启。大会荣誉主席、上海交通大学程浩忠教授代表组委会致开幕辞,主办方代表、广西大学覃程荣教授作欢迎致辞,仪式由广西大学陈碧云副教授主持。

▲上海交通大学 程浩忠教授致开幕辞

▲广西大学 覃程荣教授致欢迎辞

▲广西大学 陈碧云副教授主持会议
本次会议主会场邀请了4位学者作主旨报告,分别是:文福拴,浙江大学教授、IEEE Fellow;何怡刚,武汉大学教授、国家杰青、欧洲自然科学院外籍院士、英国皇家学会工艺院终身院士、中国电机工程学会会士;Mohamed Benbouzid,法国University of Brest教授、IEEE Fellow;黎静华,广西大学教授、国家级重大人才工程计划入选者、IET Fellow。报告与讨论涵盖电力市场、智能电网运行和维护、潮汐发电、电力系统响应控制等相关领域。

▲浙江大学 文福拴教授作主旨报告

▲武汉大学 何怡刚教授作主旨报告
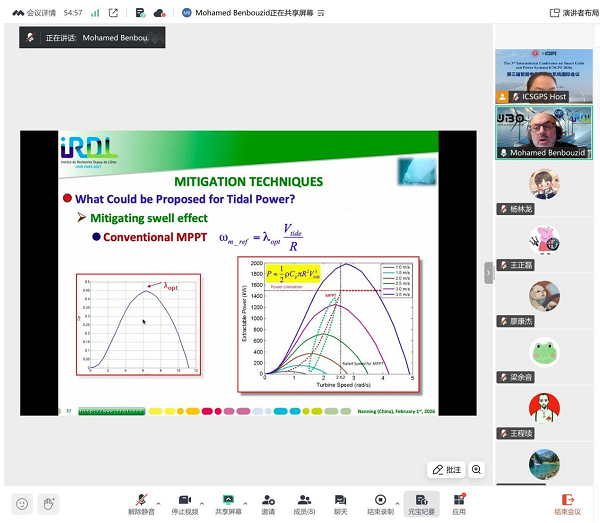
▲University of Brest Mohamed Benbouzid教授作主旨报告

▲广西大学 黎静华教授作主旨报告
其后,由广西大学张镱议教授主持学者&院长论坛,会议邀请了下列嘉宾进行分享讨论:上海交通大学程浩忠教授,武汉理工大学周克亮教授,西华大学王涛教授,广西科技大学刘胜永教授。现场互动积极,专家与听众展开了深入的学术探讨。

▲学者&院长论坛
当日下午,大会进行了分会场报告,其中4位学者作特邀报告,分别是:武汉大学刘承锡教授,武汉理工大学黄云辉教授,东北大学张孝顺副教授,武汉大学赵志高副教授。来自多所高校和科研单位的学者分享了自己的最新研究进展。报告内容丰富,交流深入,进一步增强了学术界的互通与合作。

▲武汉理工大学 黄云辉教授作特邀报告

▲东北大学 张孝顺副教授作特邀报告

▲武汉大学 赵志高副教授作特邀报告

▲华南理工大学 钱瞳副教授作报告分享

▲西华大学 王涛教授作报告分享

▲广西科技大学 刘胜永教授作报告分享

▲分会场一现场
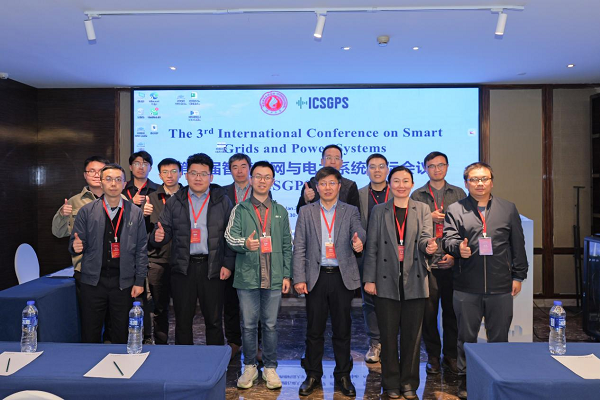

▲分会场二现场
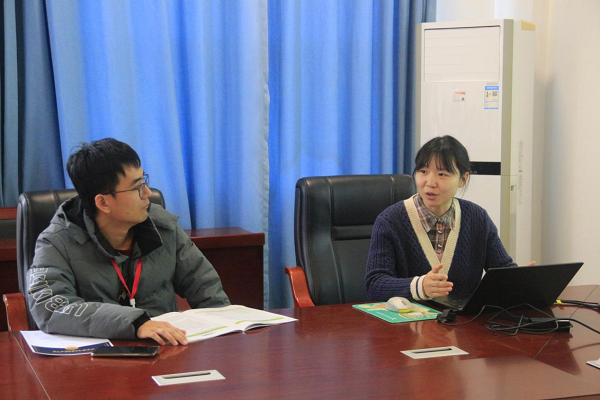

▲分会场三现场
晚上,大会举行了颁奖晚宴,对会议支持单位以及在会议投稿、论坛组织及报告学者中表现突出的组织和个人进行了现场表彰。颁发了多个奖项,以鼓励青年学者的创新探索和卓越表现。
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
晚宴颁奖现场
在活跃融洽的氛围中,主办方表达了对下一届ICSGPS会议的美好展望,期待在未来构建更高层次的国际交流平台,进一步推动国内外相关领域的创新突破与跨界融合,共迎智能电网发展的新篇章。


02-04
2026年1月24日,由中国科学院半导体研究所、江南大学主办,无锡市梁溪区政府、无锡高新区管委会、澳门科技大学、天津理工大学、中铁设计机械动力设计研究院、爱迩思出版社(ELSP)、ESBK国际学术交流中心、AC学术中心协办的第六届高性能大数据暨智能系统国际会议(HDIS)在无锡顺利召开。本次会议得到无锡高新区管委会的大力支持。
大会以“高性能大数据,智能系统”为核心主题,汇聚国内外人工智能与大数据领域的知名专家和青年学者,围绕计算架构创新、数据智能挖掘、智能感知与自主决策系统等热点方向展开深度交流,共同推动高性能计算与智能技术融合创新,助力新一代信息技术产业发展。

会议现场合照
24日上午,大会在庄重而热烈的氛围中拉开帷幕。开幕式由大会程序主席中国科学院半导体研究所宁欣研究员主持。主办单位代表即大会主席江南大学吴小俊教授以及中国科学院半导体研究所李卫军研究员分别代表组委会向与会专家学者表示热烈欢迎,并对长期关心和支持会议发展的各合作单位致以诚挚感谢。
吴小俊教授代表主办单位致欢迎辞,对来自海内外的专家学者表示诚挚欢迎,并介绍了无锡在集成电路、智能制造、新一代信息技术及人工智能产业方面的发展基础与创新生态。他希望本次会议进一步促进学术界与产业界深度融合,推动关键核心技术突破和成果转化。

江南大学吴小俊教授致欢迎辞
李卫军研究员在致辞中回顾了HDIS会议的发展历程。自创办以来,会议始终聚焦高性能计算架构、大数据分析、智能系统设计等核心方向,逐步成长为具有较高国际影响力的学术交流平台。本届会议的召开将有助于进一步加强多学科交叉合作,推动高性能计算与人工智能技术协同创新。
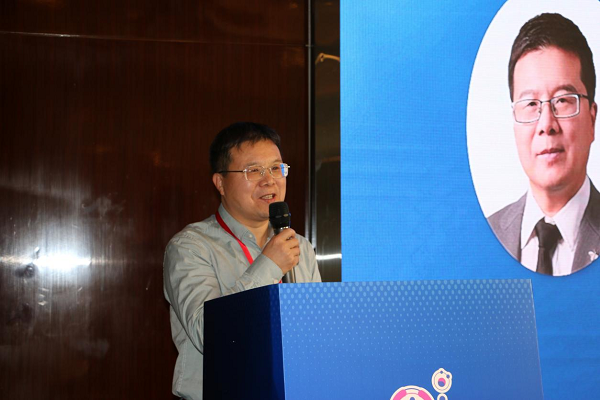

中国科学院半导体研究所李卫军研究员致辞
本届大会主会场特邀多位国内人工智能、大数据与智能系统领域的知名专家作主旨报告。报告内容紧扣高性能计算、分布式智能、信息处理与模式识别等关键方向,系统展示了相关领域的最新理论成果与工程实践,充分体现了学科交叉融合与创新发展的鲜明特征。
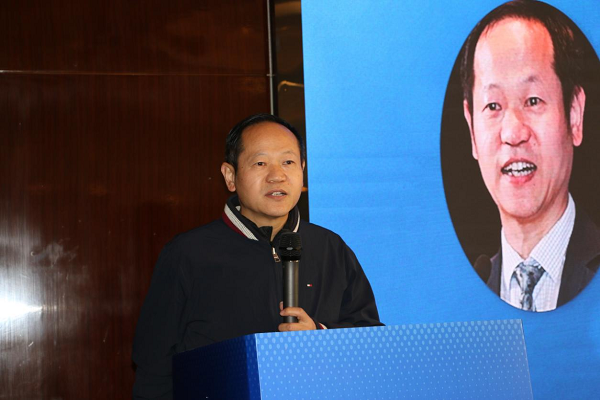
北京大学博雅特聘教授,博士生导师,IEEE Fellow,2018年国家杰出青年基金获得者田永鸿教授作题为Beyond Multimodal Foundation Models: Practical Pathways and Challenges on the Road to World Models的主旨报告。

北京大学田永鸿教授作主旨报告
随后,上海交通大学集成电路学院(信息与电子工程学院),国家级高层次人才,IEEE Fellow,AAIA Fellow,中国电子学会会士、中国计算机学会(CCF)会士熊红凯教授作题为Intelligence and Mathematics: Posteriori and Priori的主旨报告。
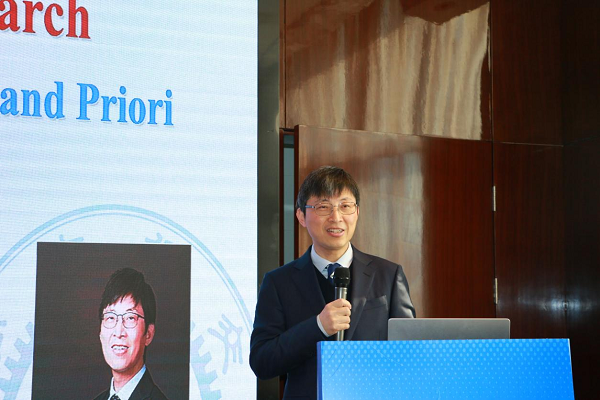

上海交通大学熊红凯教授作主旨报告
重庆邮电大学副校长,教育部“长江学者”特聘教授李伟生教授作题为Multi-dimensional Registration and Multi-modal Fusion for Spinal Surgery Image Navigation的主旨报告。

重庆邮电大学李伟生教授作主旨报告
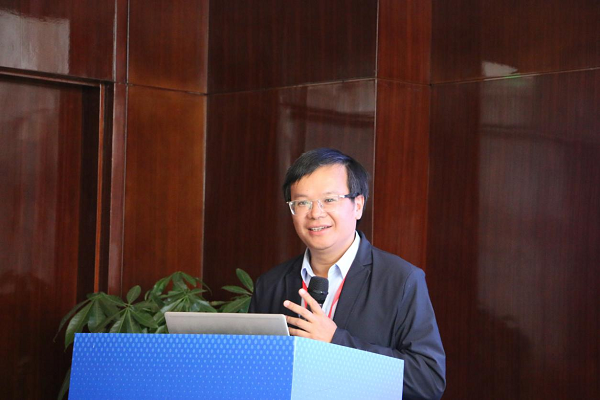
IAPR Fellow、AAIA Fellow、AIIA Fellow、NAAI 通讯院士、江南大学至善教授、研究生院院长吴小俊教授作题为Multimodal Visual Fusion and Enhancement: General Purpose Perspectives的主旨报告。

江南大学吴小俊教授作主旨报告
当日下午,大会共设立两个分会场。多项报告结合实际案例,展示了智能系统在复杂场景中的应用成效。论坛讨论环节互动频繁,围绕模型可靠性、安全性及工程部署难点展开深入交流,充分体现了学术研究与产业需求的紧密结合。青年学者和研究生积极参与成果展示,汇报内容紧贴学科前沿。现场提问踊跃、讨论深入,围绕实验设计、模型创新与工程实现等问题展开了充分交流,形成了浓厚的学术氛围。多位参会专家表示,这些研究成果体现了新生代科研力量的创新活力和扎实基础。
 |  |
 |  |
▲分会场一现场
 |  |
▲分会场现场问答环节
 |  |
 |  |
▲分会场二现场
HDIS将继续秉持开放合作、交叉创新的理念,不断拓展国际合作网络,深化学科融合,打造更具影响力的高水平学术交流平台。组委会表示,下一届会议将进一步加强与产业界的联动,推动科研成果向实际应用转化,助力智能科技创新发展。
在与会专家学者的共同努力下,第六届高性能大数据暨智能系统国际会议圆满落下帷幕。

02-04
2026年1月30日至2月1日,由中南大学主办,ESBK国际学术交流中心、AC学术平台联合协办的交通工程与控制国际会议(ICTEC 2026)在湖南长沙隆重召开。大会通过主旨报告、专题研讨与成果展示等立体化交流模式,深度聚焦交通工程与控制领域面临的共性挑战、技术范式变革与产学研升级路径。

大会现场合照
1月31日上午,大会正式拉开帷幕。大会主席——东南大学张健教授致开幕辞,强调了本次会议在推动学术交流、促进科技合作方面的重要意义,并代表组委会对远道而来的与会者表达了诚挚敬意与热烈欢迎。

东南大学张健教授致开幕辞
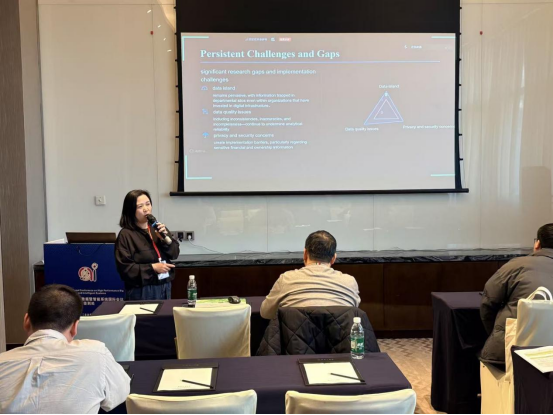
会议荣幸邀请到多位在交通工程、控制领域具有重要影响力的专家学者出席并作主旨报告。其中包括:教育部长江学者,中南大学刘辉教授;东南大学教务处副处长张健教授;山东大学齐鲁青年学者吴建清教授。此外,会议还特别邀请到了空军工程大学刘棕成副教授为大会作专题报告。各位专家聚焦交通工程与控制前沿,展示了专业领域的最新研究成果与发展动向,现场交流深入、互动热烈,充分体现了学术共同体的思想活力与创新动能。
 |  |
 |  |
▲主会场主旨报告与特邀报告
在下午的分会场中,来自多所知名高校与科研单位的学者,依次报告分享了各自的最新研究成果。报告内容兼具理论深度与实践导向,现场学术氛围浓厚,提问环节互动活跃,充分体现了学界对关键问题的深入探索与创新思考。
 |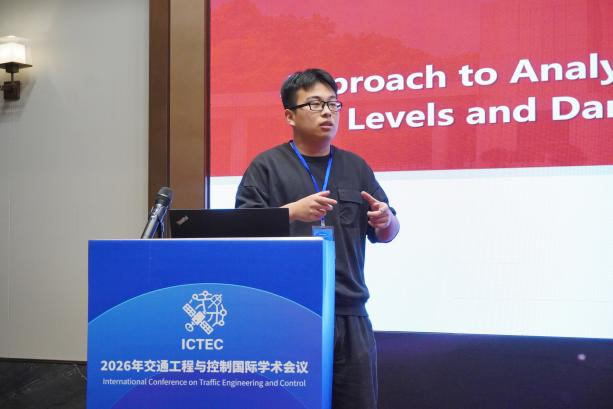  |
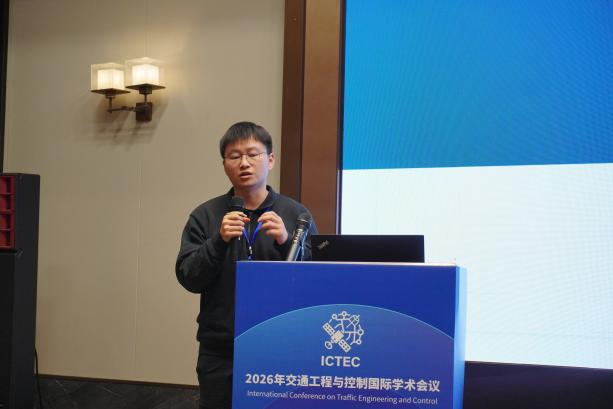 |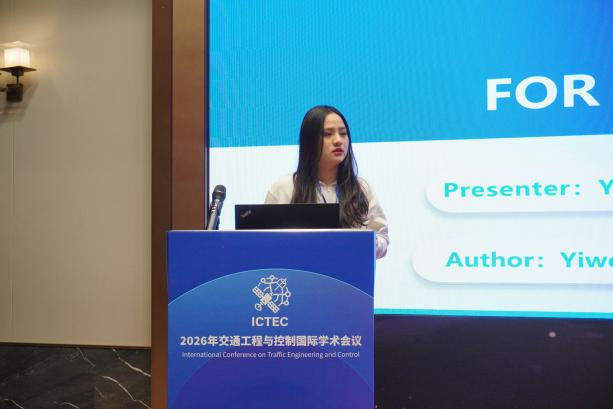  |
 |  |

▲分会场现场
大会颁奖晚宴上,组委会隆重颁授多项荣誉证书与奖章,嘉奖为本次会议作出卓越贡献的学者。他们的智慧与热忱,为盛会顺利推进奠定了坚实基础,更为学术交流注入了强劲能量。
 |  |
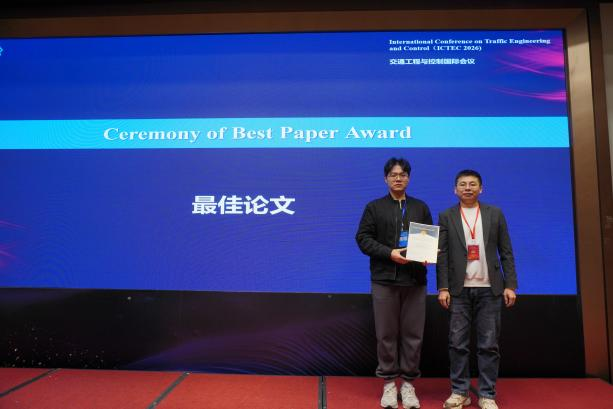 |  |
▲颁奖晚宴现场
2026年交通工程与控制国际会议(ICTEC 2026)已圆满落幕。本次会议成功搭建起交通、控制领域的高水平交流平台,汇聚众多专家学者与研究骨干,有效促进了前沿理论探索、关键技术突破与产业实践应用的深度融合。组委会表示,未来将持续整合国际优质学术资源,深化多学科交叉创新与科研协作,并期待在下一届会议上与各界同仁再度聚首,共同擘画领域发展的新篇章。

02-04
1月23日至25日,由桂林理工大学主办,西安交通大学-中国核电工程有限公司核电智能决策与预测运营技术联合实验室、江苏科技大学、ESBK国际学术交流中心、AC学术平台共同支持的第三届智能控制、测量与信号系统国际会议(FICMSS 2026)在广西南宁顺利召开。来自国内外高校、科研院所及产业界的专家学者、青年研究者齐聚绿城,分享前沿成果、研判技术趋势,推动智能控制、测量与信号系统的产学研深度融合。


大会现场
1月24日上午,FICMSS 2026在南宁隆重开幕。主会场由天津大学周圆老师主持,首先,由大会主席河海大学费峻涛教授代表组委会致开幕辞,对会议的顺利召开表示祝贺,并向给予支持的各方专家学者致以诚挚感谢。随后,桂林理工大学党委副书记黎贞崇致欢迎辞,对远道而来的各位嘉宾表示热烈欢迎,并介绍了学校在智能控制与测量技术领域的最新发展情况。

▲费峻涛教授开幕致辞

▲黎贞崇副书记欢迎致辞
本次大会汇聚了智能控制、测量与信号系统领域的多位知名专家学者。上午的主会场邀请了西安交通大学程伟教授、中国科学院自动化研究所周小虎教授、河海大学费峻涛教授和哈尔滨工程大学高洪元教授分别作主旨报告,深入剖析了人工智能控制、先进传感技术、下一代信号处理系统等前沿技术在制造业中的融合应用与发展前景。
 ▲成玮教授报告 | 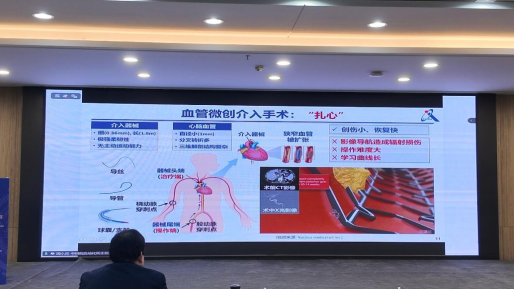 ▲周小虎教授线上报告 |
 ▲费峻涛教授报告 |  ▲高洪元副教授报告 |
除主会场报告外,当日下午大会同步举行学者报告和分会场交流,共计二十余场学术报告。与会学者围绕智能控制理论与系统、网络智能与网络控制、智能故障检测与诊断、测量信号处理与分析、高性能处理器与智能仪器、信号处理在移动通信中的应用、嵌入式系统与深度学习等热点议题展开深入研讨。来自多所高校和科研单位的报告人分享了最新研究进展,现场交流热烈,进一步促进了学术界与产业界的互通与合作。

▲分会场一现场

▲分会场二现场
12月13日晚,大会举行颁奖晚宴,为激励青年学者在智能控制、测量与信号系统领域持续创新,组委会对在会议中表现突出的单位和个人进行了现场表彰,为学科发展注入新生力量。
 |  |
 |  |
图组 颁奖晚宴现场
FICMSS 2026不仅是展示智能控制、测量与信号系统科研成果的重要平台,更是推动技术转化与学术合作的关键契机。随着人工智能、边缘计算、多源感知等技术的迅猛发展,传统测量控制技术正加速向智能化、网络化、集成化方向转型升级。FICMSS 2026的召开,为全体学者与产业界搭建了高水平的国际学术交流平台,促进了智能控制、测量与信号系统领域的深度融合与协同创新。
写好会议论文摘要(Abstract)是学术投稿的关键一步。会议的程序委员会通常要在几百甚至几千篇摘要中快速筛选出值得接受的稿件。因此,你的摘要必须在有限的字数内(通常是300-500词)清晰、有力、完整地展示研究的价值。
以下是一份 “高录用率摘要撰写指南” ,包含结构逻辑、万能句型和避坑技巧。
一、核心逻辑:摘要是一篇“微缩版论文”
不要把摘要写成“我打算做什么”的计划,而要写成“我已经完成了什么”的成果展示。
一篇优秀的摘要通常遵循 IMRaD 结构(变体),但在会议摘要中,更常见的是 B-(MR)C 结构:
1. B (Background): 背景与痛点(为什么要做?)
2. M (Method): 方法与过程(怎么做的?)
3. R (Result): 核心结果与发现(发现了什么?——最硬核部分)
4. C (Conclusion): 结论与贡献(所以呢?有什么意义?)
二、分步解析:万能句型与撰写技巧
1. 引言部分 (占 15-20%)
目标: 吸引读者,引出研究缺口,确立研究必要性。
技巧: 先给一个大背景(宽),然后迅速收缩到具体问题(窄),并指出当前研究的不足(gap)。
万能句型:
引出主题: “Recently, there has been growing interest in ...”
指出重要性: “The role of ... is critical for ...”
指出缺口: “However, previous studies have primarily focused on ..., leaving the mechanism of ... largely unexplored.” / “Despite its importance, ... remains poorly understood.”
提出目标: “Here, we aim to investigate ...” / “In this paper, we propose a novel method to ...”
2. 方法部分 (占 20-25%)
目标: 告诉审稿人你的研究是可靠的、创新的。
技巧: 如果是实验学科,写明实验模型、分组、干预手段、检测指标。如果是算法类,写明模型架构、数据集、基线对比。只要最核心的步骤。
万能句型:
数据来源: “We collected data from ... between ... and ...”
实验设计: “The participants were randomly divided into ...”
新方法提出: “We developed a novel approach based on ...”
分析手段: “To quantify ..., we performed ...”
3. 结果部分 (占 40-50%) —— 最重要!
目标: 展示你的“干货”。这是决定能否录用的关键。
技巧: 不要只说“我们得到了好的结果”,要给出具体的数据。增加数字、p值、百分比、变化率。哪怕只是初步结果,也要给出趋势。对于计算机/工科会议,这里是展示性能指标(Accuracy, F1-score, 速度提升等)的地方。
万能句型:
直接引出: “We found that ...” / “Our results demonstrate that ...”
对比增强: “Compared with group A, group B showed a significant increase in X (35.6 ± 2.1 vs. 12.3 ± 1.5, p < 0.01).”
相关性描述: “... was strongly correlated with ... (r = 0.85, p < 0.001).”
性能展示: “Our proposed model achieved an accuracy of 97.2%, outperforming the baseline by 15%.”
4. 结论与意义 (占 10-15%)
目标: 拔高研究,指出理论贡献或应用价值。
技巧: 避免简单地重复结果。要说明结果意味着什么,以及对领域有什么影响。
万能句型:
总结结论: “These findings suggest that ... plays a crucial role in ...”
指出贡献: “This study provides the first evidence that ...” / “Our work offers a new framework for ...”
应用前景: “This approach could potentially lead to the development of ...”
三、让摘要脱颖而出的 5 个“潜规则”
1. 关键词轰炸: 在摘要的合理位置,尽可能多地植入会议主题中的热门关键词。这样在程序主席(Chair)分配审稿人时,你的文章更容易被分到对口的小领域,而不是被打酱油的审稿人拒掉。
2. 结果前置: 许多顶级会议摘要要求在开头或标题中就亮出结论。不要像侦探小说一样把结果藏到最后,学术写作是倒金字塔结构。
3. 精准引用: 如果会议允许在摘要中加引用,引用1-2篇该会议往届的高水平论文或领域大牛。这暗示你的研究是建立在该会议/领域基础上的,容易获得好感。
4. 逻辑连接词: 使用显眼的逻辑连接词引导审稿人思路,让他在30秒扫读中就能抓住重点。
为了引出问题: However...
为了引出方法: Here, we...
为了引出结果: Interestingly / Notably...
5. 反复检查“Deadline”: 严格遵守字数限制和格式要求(字体、行距、是否匿名)。格式错误是直接被 Desk Reject(直接拒稿)的最低级理由。
四、需要避免的常见误区
❌空泛的口号: “The results will be discussed.”(太虚了,结果就是现在要展示的)。
❌过多的背景介绍: 写了半天的历史回顾,结果没地方写自己发现了什么。
❌缩略语不加解释: 第一次出现必须写全称(除非是领域内公认的DNA, RNA这种)。
❌抄袭复制: 即使是自己的已发表论文,直接复制粘贴摘要(如果会议要求原创)也可能导致退稿。
❌语法错误: 这是学术不严谨的直接体现。写完后用Grammarly等工具检查一遍,或请导师/同学润色。
五、投稿前的检查清单
在点击提交按钮前,请对着镜子问自己:
1. 我的核心结论在第一眼能看到的地方吗?
2. 摘要中有没有具体的数字/数据支撑?
3. 有没有指出这项研究的创新点或填补了什么空白?
4. 是否包含了会议要求的所有要素(如伦理声明、基金号等,如有要求)?
5. 标题是否足够吸引人且准确概括了内容?
总结:一篇易录用的摘要 = 清晰的痛点 + 创新的方法 + 亮眼的数据 + 明确的意义。用最精炼的语言,讲一个完整且精彩的故事。
对于刚开始接触学术写作的新手来说,确实很容易把摘要(Abstract)和引言(Introduction)搞混。它们看起来都在文章的开头,但功能、内容和读者阅读的目的完全不同。
最核心的区别可以用一句话概括:
摘要是你论文的“迷你版”,而引言是你论文的“开场白”。
以下是详细的对比指南,希望能帮你理清思路:
核心目的对比
摘要: 让读者决定“是否要读全文”。
- 它是一篇独立的短文,总结了全文的精华。读者看了摘要,就应该知道你这篇文章做了什么、发现了什么。
引言: 让读者理解“为什么要做这个研究”。
- 它引导读者进入你的研究领域,展示现有研究的空白,并证明你的研究为什么重要。
内容结构对比
摘要的结构(通常是高度浓缩的线性结构):
1. 背景: 1句话交代大背景。
2. 问题/目的: 你要解决什么问题?
3. 方法: 大概怎么做的?(用了什么材料、数据、模型)
4. 主要结果: 最关键的数据或发现是什么?(通常是定量的)
5. 结论/意义: 这个发现说明了什么?
引言的结构(通常是漏斗形结构——由宽到窄):
1. 大背景: 研究领域是什么?为什么重要?
2. 文献回顾: 别人已经做到了什么程度?
3. 研究缺口: 别人没做什么?现存问题是什么?(这是关键转折点)
4. 研究问题/目的: 因此,本文打算做什么?
5. 研究路线: 本文的架构是什么?(可选,有时放在末尾)
6. (有时包括)主要发现预告: 提前告知主要结论,但这部分在引言中通常很简略。
关键区别一览表
| 维度 | 摘要 | 引言 |
|---|---|---|
| 长度 | 极短(通常 150-300 字,有严格限制) | 较长(通常 1-3 页,视学科而定) |
| 内容 | 包含结果和结论 | 不包含具体的结果和结论(仅预告) |
| 独立性 | 完全独立。可以不读全文就能看懂 | 依赖全文。需要读后面才知道具体结果 |
| 读者心态 | 想快速了解核心发现 | 想了解研究背景和动机 |
| 参考文献 | 一般不引用参考文献 | 必须引用大量参考文献 |
写作时态与时态问题(易错点)
摘要: 混合时态。
- 背景: 现在时 (The problem is...)
- 方法/结果: 过去时 (We conducted..., The results showed...)
- 结论: 现在时 (These findings indicate...)
引言: 主要是现在时和现在完成时。
- 介绍公认事实: 现在时 (Photosynthesis is...)
- 引用前人研究: 现在完成时 (Previous studies have shown...)
- 本文目的: 过去时或现在时 (This paper aims to...)
新手容易踩的坑
1. 把引言写成摘要:
- 错误做法: 在引言最后一段详细列出实验数据和图表结果。
- 正确做法: 引言只负责提出问题,不负责解答问题。结果要留给“结果与讨论”部分。
2. 把摘要写成引言:
- 错误做法: 摘要里花了大量篇幅介绍背景和文献回顾,最后只写了一句“本文发现了有趣的现象”。
- 正确做法: 摘要里必须写出具体的数据和结论,比如“实验结果显示,A物质使B物质的产量提高了50%”,而不是只说“实验结果显示A物质有影响”。
3. 摘要有引用:
- 除了极少数特殊情况(如评论性文章),摘要中不要出现“(张三,2023)”这样的引用。
新手写作顺序建议
很多新手会从引言开始写,然后卡住。推荐的写作顺序是:
1. 先写: 论文的正文(方法 -> 结果 -> 讨论)。因为这时你对研究的细节最清楚。
2. 再写: 引言。根据你的结果和讨论,反向思考你需要铺垫什么样的背景。
3. 最后写: 摘要。等到全文写完,你才知道这篇文章最核心的贡献到底是什么,才能写出最准确的摘要。
总结记忆法
- 摘要 = 地图: 给你一张完整的缩略图,告诉你整个旅程的起点和终点。
- 引言 = 路标: 告诉你为什么要出发,以及在这个领域里,这条路为什么值得走。
针对2026年高校财务报销的严格趋势,国际会议注册费发票的类目选择和报销要点如下:
一、 首选类目:“会议费”
这是最合规、最不容易被审计退回的类目。
- 关键依据: 只要是参加学术会议产生的注册费用,无论发票内容写的是“注册费”、“参会费”还是“会议费”,在财务处理上都应计入“会议费”科目。
- 避坑提示: 有些国外的电子发票或收款凭证可能不显示具体类目,仅显示为“Registration Fee”。报销时,通常需要附上会议官网的注册说明(显示该费用包含参加 sessions、领取会议资料等内容)作为佐证,以证明其属于会议性质。
二、 备选类目:“注册费”/“技术服务费”
- 适用场景: 部分高校的财务系统对“会议费”有严格的预算限制(如必须附会议通知、必须单独审批),或者发票确实只开了“服务费”。
- 处理建议: 在发票确实无法更改且“会议费”额度不足的情况下,可尝试归入“注册费”或“版面费/出版费”(如果该会议有出版论文集且你是作者之一)。但需注意,如果只是单纯听会而没有发表文章,归入“版面费”会有审计风险,不建议轻易使用。
三、 高校财务2026年特别避坑指南
1. 警惕“代转”陷阱(关键!):
- 很多国际会议使用第三方支付平台(如PayPal、信用卡支付)或国内代理公司收款。如果是由国内代理公司代收并开具发票,类目很可能是“代订服务费”或“会务服务费”。
- 注意: 这种发票在2026年的审计中可能会被质疑。因为“服务费”属于商业行为,而高校教师的差旅通常要求直接费用。解决方法:必须附上会议主办方委托该代理公司收款并转付注册费的《委托协议》或官网截图,否则可能被认定为“违规转包”不予报销。
2. 外币支付凭证务必保留:
- 国际会议通常是线上支付(美元/欧元)。报销时,不仅需要发票(Invoice/Receipt),银行扣款回单(或信用卡账单)必须作为附件。如果发票金额是100美元,但实际信用卡扣款是105美元(含手续费),高校财务通常只报销发票面额,手续费需单独说明或自理。
3. 电子发票重复报销核验:
- 2026年高校财务系统已全面联网查重。如果是通过国内代理开具的电子发票(PDF/OFD),提交前务必确认财务系统没有“查重”提示,防止同一张发票被不同项目组重复使用。
总结:最稳妥的做法是要求对方开具内容为“会议费”的发票。如果对方是境外机构只能提供Receipt,则在报销单上选择“会议费”科目,附上支付记录和会议通知即可。
版面费和会议注册费是学术研究中两种完全不同的费用,主要区别在于支付的场景和费用的用途。
简单来说:版面费是让你在期刊上发表文章的钱;会议注册费是让你去开会(听报告、拿资料、吃饭)的钱。
以下是详细的对比:
1. 版面费 (Page Charge)
- 发生场景: 期刊投稿(如SCI、EI期刊、国内核心期刊等)。
- 支付目的: 为了让你的论文在通过同行评审后,能够在期刊上正式排版、印刷和在线发布。
- 支付时间: 论文被接收后、见刊/发表前。
- 费用流向: 支付给学术期刊出版商(如Elsevier、IEEE、MDPI,或者国内期刊社)。
- 服务内容: 相当于支付了“出版成本”。包括:排版校对、语言润色(部分包含)、转换成XML格式、在数据库上线永久保存等。
- 是否必须: 如果不交,论文通常无法正式发表(除少数传统订阅期刊不收版面费,但读者需要付费订阅)。
2. 会议注册费 (Registration Fee)
- 发生场景: 学术会议(如国际会议、学会年会、研讨会)。
- 支付目的: 为了让参会者获得入场资格以及会议期间的服务。
- 支付时间: 会议开始前(通常有早鸟优惠)或会议报到当天。
- 费用流向: 支付给会议主办方(通常是大学、学会或会议组委会)。
- 服务内容: 相当于购买了“参会体验”。包括:会场入场证、纸质或电子版的会议议程/论文集、会议期间的茶歇、午餐、晚宴,以及纪念品等。
- 是否必须: 即使论文被会议收录(发表会议论文),通常至少需要有一位作者注册缴费,否则论文可能不会被收录进论文集或安排报告。如果是只想旁听不投稿,也要缴费才能入场。
3. 关键区别总结
| 维度 | 版面费 | 会议注册费 |
|---|---|---|
| 核心用途 | 让你的文章变成铅字(出版) | 让你进入会场(参与) |
| 支付对象 | 出版社/期刊社 | 会议组委会/承办方 |
| 费用构成 | 排版费、OA(开放获取)处理费 | 餐饮费、物料费、场地费 |
| 支付节点 | 论文录用后 | 注册参会时 |
| 金额特点 | 通常较贵,OA期刊动辄上万元 | 视会议规格,几百到几千不等 |
| 可选性 | 想发表就必须交 | 想参会就必须交 |
特别提醒
- 关于会议论文: 如果你投的是一个学术会议,通常你交的注册费里已经包含了出版你那一页摘要或短文的费用。这种情况下,一般不会再单独向你收取一笔“版面费”,注册费就是全部费用。
- 关于高价OA: 如果你投的是Open Access(开放获取)期刊,版面费可能会很高(有时超过2万元人民币),但这和会议注册费是完全分开的两笔开销。
合作伙伴